Did you know that children were not considered a child in mediaeval times? Yes, you read that right, near seven years of age, a child was considered a "little adult" who is capable of carrying out any action like an adult, such as legal consequences, doing a job and even marriage. It sounds a bit absurd, but it's true!
But in the 20th century, Jean Piaget's cognitive development theory came forth to revolutionise the above mentioned concept. If you are wondering about the meaning of Cognitive development–it is a field of study focused on a child's development. Cognitive development indicates how a child's brain works and how he analyses and identifies things around him.
Psychology's cognitive development researches the interior mental processes of people and animals, such as memory, reasoning, problem-solving, communication, and decision making. This method is known as cognitivism, and cognitivism psychologists are concerned with how information is gathered and how it affects human behaviour.
Jane Piaget emphasised the truth that children are not merely little grown-ups and that their thought processes are fundamentally distinct.
Piaget thinks of children as "little scientists" rather than the "little adults" who study everything around them in order to receive a finer awareness of their surroundings. Piaget also considered that kids acquire such knowledge on their own, without the support of the grown-ups. He suggested that minors acquire wording and memories and develop a thought process independently, part of their evolution.
He had laid down the 4 stages of development. Read the full blog as it is explained in depth by our nursing assignment help experts.
What Are the Different Developmental and Psychological Ranges?
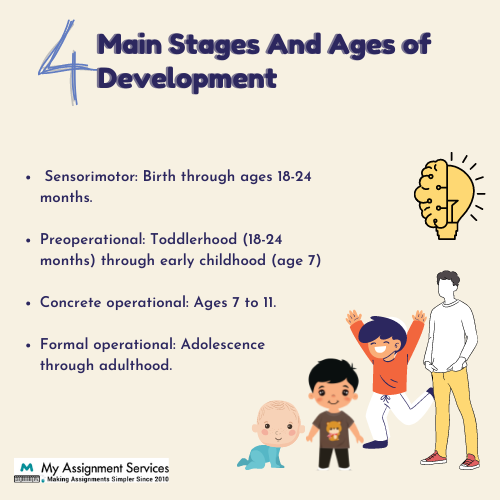
Stage 1: The Sensorimotor Stage, from birth to 2 years.
This is the very first stage, where babies use their senses and body gestures to decipher what is happening around them. From their birth to two years of age, they only use their senses to grasp everything. This is the reason why this developmental rage is known as the sensorimotor stage.
You can also observe the primary reflex activities such as swallowing and shaking the head flailing limbs at this stage. These are infants' earliest norms of communication. They explore their setting and bodies via their five senses of vision, feeling, taste, smell, and listening.
Infants understand how various things help them feel as they absorb knowledge about these encounters. They also formulate the capacity to characterise between people, items, surfaces, and illustrations.
They begin to comprehend the notion of action and reaction at this age. They understand that each activity will result in a clear matter and utilise this knowledge to prepare ahead of time.
They will begin to seize object permanence at the mere age of six months. This suggests the children apprehend that items exist even when they can't see, listen to, or feel them.
When a kid conceives understanding of the objects around them, it indicates that instead of reacting to events in their direct surroundings, they may now create a cognitive illustration, or description, of such an object in their head.
Learn how to acknowledge any source of information using the APA 7th style.
Download Now
Stage 2: The Preoperational Stage, between 2 to 7 years
At a pre-operational stage, infants strive to evolve to abstract how the brain approaches while creating object permanence. This suggests that they can consider things other than the physical world as occurrences in the past.
They also envision and think figuratively, and their vocabulary and behaviour begin to reflect this capability.
You must have seen the below-mentioned 4 behaviours in every child that you have contacted at this stage:
- Copying Actions: You must have seen children imitating actions at this stage.
- Symbolic Play: Children categorise objects according to their understanding. You might have seen them give names to their toys and associate them with some living or non-living object.
- Scribbling: Every house with kids between 2-and 7 years old has a wall scribbled with the artwork. The unnecessary scribbling and drawing show that they are learning and adapting things.
- Mental Imaging: When children start to learn and go to school, their imagination power is strong. If you teach them about lions, they will associate them with any cartoon or comic characters to memorise and learn faster.
Centration occurs when a youngster concentrates solely on one component while neglecting the other. For example, if a youngster is presented with two identically sized cups of water, he or she will recognise that they are the same. However, if one of the cups of water is put into a bigger glass, the youngster perceives that the bigger glass contains more liquid than the other, despite the fact that the volume of water remains the same.
Stage 3: The Concrete Operational Stage, between ages 7 to 11.
At this point, the youngster can adapt to predefined rules but only through tangible instances. This is shown by the idea of "conservation," which occurs when the amount of a thing remains constant despite a change in appearance. By this age, a youngster can use logical rules and recognise that the volume of water in the higher glass, as well as the previous glass, is the same. Piaget thought that a kid at this time could not grasp theoretical or abstract questions since the child's comprehension was restricted by his or her physical world experience.
According to Piaget, egocentrism is the incapacity to perceive things from someone else's viewpoint, and the youngster only looks at things from his own. Piaget did an experiment to test this notion; he used a basic plaster mountain range, positioned a kid on one side of the model, and asked the youngster to tell him whatever Piaget had seen.
Stage 4: The Formal Operational Stage, from 12 to above.
A youngster may now use conceptual and methodical thought to difficulties when working out issues. This comes between stages 3 and 4. When a kid is given a solution to deal with, a stage 3 brain will create a plan and attempt different permutations to solve it. Still, a stage 4 thinker will create a plan, apply a principle, create a hypothesis, and verify it to validate the result.

Final Words from The Experts Regarding The 4 Stages of Human Development
Finally, the cognitive approach investigates human and animal internal mental processes, as well as how the knowledge we process influences our learning and behaviour. One of the key contributions to this viewpoint is Jean Piaget, who is well renowned for his beliefs on a child's intellectual development. His view was that a child's development happens in four stages: Sensorimotor, Pre-Operational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational.
He felt that assimilation processes produced these modifications. Piaget argued that the Sensorimotor and Preoperational stages were the most essential since they shaped the infant's developmental learning. His theory hypothesis was first ridiculed by many, but over the last 100 years, it has been proven effective and can be observed in a lot of studies involving a child's growth.
This field of study requires extensive research and study, although our experts have tried their best to demonstrate it to you; if you need more information on this to score HD grades in your assignment or test, you can reach out to experts for a guided learning session, you can also connect with them for any nursing assignment help. All you have to do is fill out the form given on the screen.
Related Study Materials
Our Experts can answer your Assignment questions instantly.
Ask Question0 Comment
Get It Done! Today
1,212,718Orders
4.9/5Rating
5,063Experts













Loved reading this Blog? Share your valuable thoughts in the comment section.
Add comment