
Three types of respiration occur in various living organisms on earth, internal, external, and cellular. Cells of both autotrophic and heterotrophic beings respire at a cellular level. Cellular respiration aims to convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This conversion of elements generates energy at a cellular level. The two major forms of respiration are aerobic cellular respiration and anaerobic cellular respiration. We’ll see the definition of both of these. Through this blog, we will help you understand how aerobic and anaerobic forms of cellular respiration are different from each other via examples.

Aerobic Respiration
The process in which organisms use oxygen to breathe and for breaking down fats and glucose into the chemical form of energy is called aerobic respiration. They respire at a cellular level to generate power inside the cell through an exchange of gases. The molecule named adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is produced during respiration. ATP is often called the energy currency or fuel of the cells as it initiates chemical reactions in phosphate bonds to dispense the energy stored in them. It is an efficient form of breathing as a large amount of ATP is produced in a short period. This is due to the presence of oxygen. More electrons are exchanged in the reaction due to the use of oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
When cells break down sugars and other elements to generate energy in the lack of or deprivation of oxygen, it is called anaerobic respiration. It is a less efficient form of respiration than aerobic respiration, as a very low amount of ATP is produced. Oxygen is effective and useful in electron exchange at the molecular level during cellular respiration. Many organisms have evolved to perform respiration without oxygen and exchange electrons using other elements.
But How Are the Two Forms of Respiration Different From Each Other?
As we discussed above, aerobic respiration occurs in cells of organisms who exist in environments with abundant oxygen levels; aerobic respiration is different from anaerobic respiration in the following ways:
- Except for some primary prokaryotes, aerobic respiration happens at the cellular level for humans, animals, and plants.
- Oxygen is an affinity for accepting electrons; hence, more ATP is produced quickly in anaerobic respiration.
- Double oxygen bonds are the reason for producing a large amount of ATP.
- A Kreb cycle occurs during aerobic respiration, which means pyruvate and glycolysis degenerate in mitochondria and are completely oxidized.
- Carbohydrates are oxidized by using fats and proteins as reactants during aerobic respiration.
- Carbon dioxide and water are released in aerobic respiration, and another phosphate element is added to ADP for ATP formation.
- The NADH molecules and FADH2 molecules are degenerated to be converted into
- The oxygen molecule pumps protons out of the cell membrane during aerobic respiration.
- 38 ATPs are given out during aerobic respiration, whereas due to energy loss only 30 ATPs remain.
- The carbohydrate molecules are wholly oxidised inside the mitochondria of a eukaryotic celled organism.
Learn how to acknowledge any source of information using the APA 7th style.
Download Now
Anaerobic respiration happens without a high electron acceptor of oxygen, so a low ATP is produced. Here’s the entire process of how aerobic respiration takes place:
- Either sulfate (SO4–) or nitrate ions (NO3–) are responsible for electron movement during anaerobic respiration.
- Single-cell organisms like archaea use carbon dioxide to accept electrons and leave methane as the by-product.
- Sulfur bacteria release hydrogen sulfide as they use sulfate as an electron acceptor.
- Prokaryotic single-celled organisms exist in a low-oxygen environment, so they depend on anaerobic respiration to break down components.
- The only way aerobic and anaerobic respiration is similar is that the chemical reaction for both forms of respiration uses an electron acceptor to break down components.
- The electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration has less electron acceptor affinity than oxygen; therefore, less ATP is produced.
- Carbon, nitrogen, and biogeochemical sulfur use anaerobic respiration to fix these gases in the environment.
- Nitrogen gas is produced by using nitrate ion as an electron acceptor and is crucial for environmental nitrogen fixation.
- An example of anaerobic respiration fermentation is partial oxidation of glycolysis molecules and pyruvate due to the citric acid cycle.
- NADH is not utilized in fermentation.
- Soil, deep-sea waters, and freshwaters are where anaerobic respiration takes place as oxygen does not get completely dissolved in these surfaces, thus causing a lack thereof.
- Only two ATPs per glucose molecule are produced during fermentation.
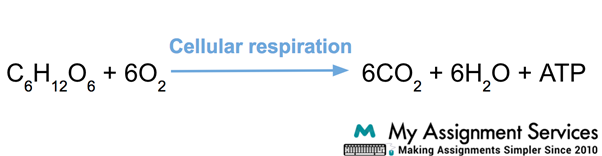
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Assignment Samples


Following are a Few Examples of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration Examples
Human respiration:
- Humans respire through aerobic respiration. A breakdown of glucose happens due to oxygen in our body that produces energy inside the cells.
- The original degradation of components occurs inside the cytoplasm; the by-products then move to mitochondria to produce ATP.
- Lungs absorb oxygen that gets further dissolved in the red blood cells, which helps in cellular level aerobic respiration.
- During cellular respiration in humans, carbon dioxide is produced.
- Oxidation of carbohydrates using oxygen for producing energy during aerobic respiration for humans.
Anaerobic Respiration Example
- For bacterias like Propionibacterium shermanii, propionic acid fermentation occurs when they break down carbohydrates and give out carbon dioxide and propionic acid.
- The fermentation process of swiss cheese is the most common example of this form of anaerobic respiration.
- Carboxylic acid is produced due to carbon dioxide during fermentation, giving it a distinct taste.
- Anaerobic respiration occurs similarly for all single-celled prokaryotes due to lack of oxygen.
Struggling to Finish Your Biology Assignment? Get Help from Our Experts
We hope that our discussion about the differences and examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration in the blog was helpful for you. These forms of respiration are good examples of the oxygen equation for the breakdown of carbohydrates during cellular respiration. We further learned how the organisms breathe and break down their food even in a lack of or no oxygen. Writing biology assignment answers on this topic comes with its challenges, which you have to face and overcome to obtain desired grades in your course. Of course, online resources such as blogs, biology assignment samples, video tutorials, and articles are an excellent source of information for writing your assignments. But, you will still need to understand a range of complex concepts while doing so. Hire our academic assistance and we will guide you through our one-to-one guided sessions. Our biology experts are available 24*7 and will be available to assist you during any odd time of a day. To connect with us, simply fill in the form and upload your assessment file!
Related Study Materials
Our Experts can answer your Assignment questions instantly.
Ask Question0 Comment
Get It Done! Today
1,212,718Orders
4.9/5Rating
5,063Experts












Loved reading this Blog? Share your valuable thoughts in the comment section.
Add comment