
Mitosis is a process in which the chromosomes are replicated so that each cell contains the identical number of chromosomes as its parent cells. On the other hand, meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. The two processes are both important but serve different purposes. One way to remember this difference between mitosis and meiosis is to think about mitosis as a "copy" since it replicates the original set of chromosomes present in each parental cell to produce daughter cells with identical sets. On the other hand, Meiosis can be thought of as a "mix" due to its purpose being to mix together genetic material from parents to produce offspring with combinations of traits not present in either parent.
The process of mitosis is found in all living organisms. Mitosis creates daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. Meiosis occurs during sexual reproduction and produces haploid gametes (sperm or egg cells). These specialized cells contain only half the number of chromosomes as a regular body cell, so when two gametes merge at fertilization, they produce a complete diploid set of chromosomes. Let's find out an overview of mitosis vs meiosis. overview of mitosis vs meiosis.
Mitosis vs Meiosis: Comparison
- Mitosis is a type of cell division that replicates the original set of chromosomes present in each parental cell to produce daughter cells with identical sets, while meiosis, on the other hand, reduces the chromosome number by half.
- In mitosis, a single chromosome of each pair is present in each resulting daughter cell while both homologous chromosomes are present in a single nucleus in the meiosis I phase, and each gamete produced by meiosis has only one-half the number of chromosomes found in a diploid germ cell.
- Mitosis occurs during mitotic division or when growth is completed, and cells have to divide to produce two identical daughter cells. It is responsible for the reproduction of somatic cells, i.e., all cells except sperm and ova, which go through the meiosis II division phase prior to fertilization. On the other hand, Meiosis occurs in germline cells that have gone through the DNA replication phase but didn't undergo chromosomal crossing over the phase where genetic recombination takes place. As a result, meiosis I form one diploid (2N) germ cell with the same number of chromosomes found in parental cells, while meiosis II splits these homologous chromosomes into separate haploid (1N) gametes.
- Mitosis doesn't involve the process of crossing over that occurs during the meiosis I or II phases, while both crossing over and chromosomal crossover take place during the prophase stage in Meiosis I & II divisions.
- Mitosis requires growth to occur in a culture, or it can be seen during the formation of gametes (producing sperm and eggs), while meiosis occurs in germ cells that have already replicated their DNA prior to fertilization.
- In mitosis, prophase takes place every day while this stage is skipped in meiosis I division since prophase takes place only once at the start of every cell cycle. In meiosis II, a similar phase called prometaphase happens before anaphase, which results in progress toward metaphase, whereas mitotic division doesn't involve the process of prometaphase.
- Meiosis I produces 4 haploid cells with half the number of chromosomes found in parental diploid cells, while mitosis produces two daughter cells with an identical number of chromosomes found in parental cells. Furthermore, Meiosis II produces 4 haploid cells with only half the number of chromosomes found in diploid germ cells.
- Mitosis occurs at the end stage when growth is completed, and dividing cells are required to produce two sister daughter cells that are similar to each other, whereas meiosis takes place at the beginning stage when gametes are produced for fertilization. Therefore, fertilized egg or zygote formed during sexual reproduction will undergo mitotic division at successive stages leading to the development of the embryo.
What are the Similarities Between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Both mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division, resulting in the formation of daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and their parent cell. The difference between them is that mitosis takes place during the growth stage while meiosis occurs at different stages depending on the type of germline cells involved, i.e., spermatogonia, oogonial stem cells or primary oocytes, due to the fact that they have already replicated their DNA prior to the formation of gametes (sperm or egg). Mitosis and meiosis involve two steps for completion, which are known as karyokinesis and cytokinesis, respectively, where daughter chromosomes/cells remain together until a complete set is formed. During cytokinesis, the mitotic spindle disintegrates into fragments that are removed after splitting interconnected cells. On the other hand, the meiotic spindle doesn't split completely but remains connected by a cytoplasmic bridge until all chromosomes/cells reach their respective poles.
During mitosis and meiosis I division phase, sister chromatids separate to form two equal diploid daughter cells, while during the meiosis II phase, homologous chromosomes separate, resulting in four haploid gametes with half the number of chromosomes found in parental cells. However, both mitosis and meiosis result in the formation of genetically identical daughter cells, which play an important role in the growth, reproduction or development of offspring where fertilization takes place between male and female germ cells for this purpose.
The meiosis II phase is preceded by meiotic interphase, where DNA replication takes place prior to the formation of sister chromatids in prophase I. Mitosis doesn't involve any type of interphase stage, whereas both mitotic and meiotic divisions take place only once during every cell cycle due to the fact that they are non-dividing stages, unlike G2 or S phase involved in cell growth and DNA replication, respectively.
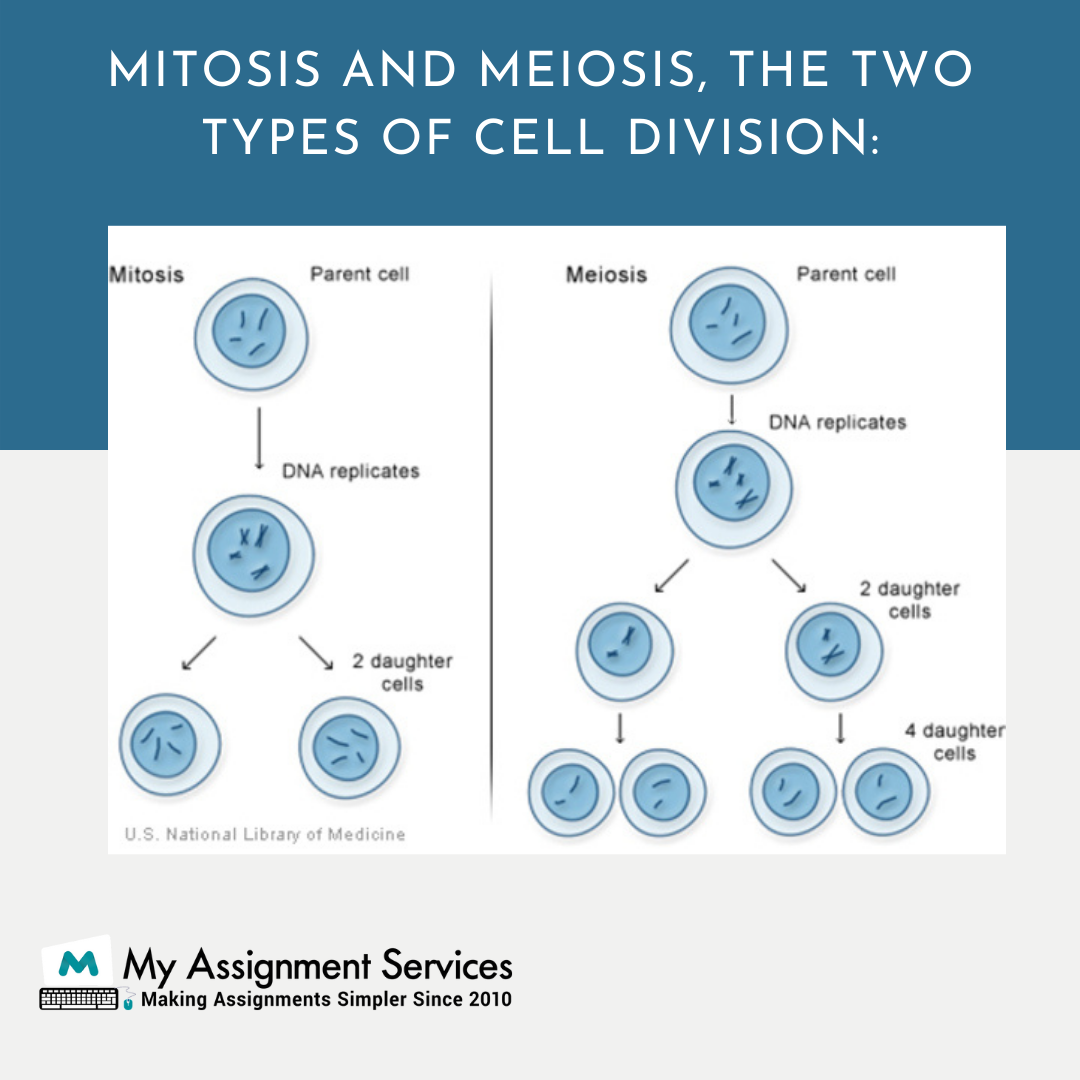
Both mitosis and meiosis start with metaphase followed by anaphase, prometaphase, metaphase, telophase and cytokinesis, where chromosome movement during division phases differs in these two types of cell divisions, i.e., centromere movement during mitosis leads to the formation of two identical daughter cells, whereas sister chromatids move towards opposite poles during meiosis I or II resulting in the production of four haploid gametes.
Mitosis occurs at a later stage of development when growth is completed. Cells are required to produce two genetically identical daughter cells which will replace themselves. At the same time, meiosis takes place early in development where germline cells are produced for fertilization purposes after replication of DNA prior to division, i.e., spermatogonia undergo mitotic division at successive stages leading to oogenesis, production of female germline cells called oocytes where meiosis begins with prophase followed by metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis resulting in the formation of four haploid ova containing half number of chromosome found in parental cells, i.e., 23 homologous chromosome pairs found in the human body.
Need Academic Guidance On Mitosis vs Meiosis? Here you Go!
Both mitosis vs meiosis are two types of cell divisions that occur in somatic (body) cells after the formation of four daughter cells, whereas germline cells divide by meiosis at successive stages leading to the production of haploid gametes, each containing only one set of homologous chromosome pairs. Therefore, mitosis is a non-dividing stage where only two daughter cells are produced, while meiosis takes place at different stages due to the fact that it produces four haploid gametes. Also, centromere movement during mitosis leads to the formation of two identical daughter cells, whereas sister chromatids move towards opposite poles during meiosis I or II resulting in the production of four haploid gametes with half the number of chromosomes found in parental cells.
We know that sometimes it's hard to find the time or motivation to complete your assignments on either mitosis or meiosis. That is why My Assignment Services has a team of experts ready and waiting to guide you with all aspects of any assignment, from brainstorming ideas for research papers, organizing data sets into graphs and spreadsheets, editing drafts before handing them in, or creating presentations using PowerPoint. Just contact us by filling the form!
Related Study Materials
Our Experts can answer your Assignment questions instantly.
Ask Question0 Comment
Get It Done! Today
1,212,718Orders
4.9/5Rating
5,063Experts













Loved reading this Blog? Share your valuable thoughts in the comment section.
Add comment