A summation can be defined as the after-effects of several electrical impulses transmitted through a junction composed of nerve and muscle cells (also known as neuromuscular junction). A single stimulus is not strong enough to activate a body function, but many stimuli together can evoke a response. In order to achieve action potential, the required voltage of electrical stimulation must be achieved. The threshold is attained by temporal and spatial summation put together.
Temporal summation occurs in the nervous system when a particular neuron receives repeated stimulation to achieve an action potential. For temporal summation, newer summations rise before the previous potential moves down the synapse. The former potential and the newer potential that follows will generate a larger action potential. When this occurs in the nervous system, multiple stimuli reach the action potential threshold, starting a new action potential. The sub-thresholds that combine to generate action potential are called excitatory postsynaptic potential or EPSPs. The action potential is generated only when all sub-thresholds together can equate to the suprathreshold.
The temporal summation facilitates successive PSP integration. It can be elaborated by shooting action potentials in a presynaptic neuron and analysing the resulting EPSps.
The neuron receives stimuli from other cells with nerve cells for spatial summation to achieve an action potential. When the sub-threshold of presynaptic neurons generates a response on the postsynaptic neurons, it is a spatial summation. This type of summation requires many EPSPs for producing action potentials in the nervous system. In some cases, the excitatory and the inhibitory postsynaptic can sum up together in the postsynaptic potential that prevents the generation of action potentials; this is called postsynaptic inhibition.
When the strength of muscle contraction changes by changing the size and quantity of motor units, these motor units help maintain a continuous when some are counter, and others are relaxing, which helps defy the fatigue that the body experiences.
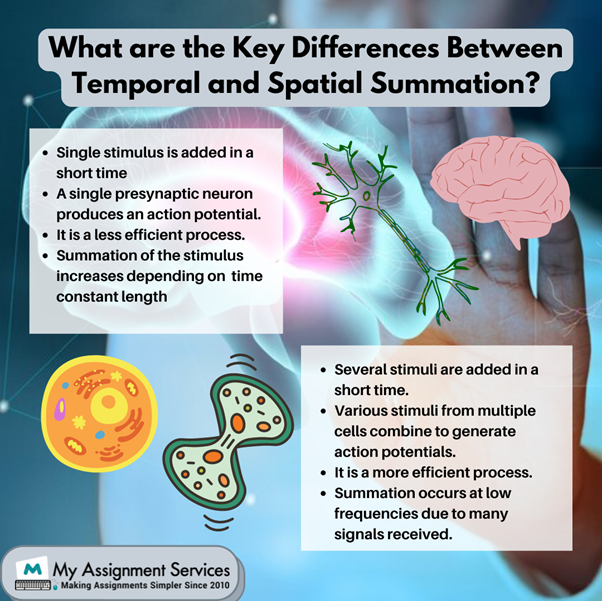
Temporal vs Spatial Summation: List of A Few Similarities and Differences
Similarities
- Both forms of summation occur in the nervous system, resulting in a body response.
- Be it simultaneous or repetitive multiple stimuli combine to generate an action potential.
- Multiple sub-thresholds are involved that are added together to create a suprathreshold.
- Any of these summation forms increases the probability of achieving the threshold to generate action potentials; in a way, both have the same purpose.
- Summation in the nervous system activates the motor units that evoke a response in a body function form. For example, the multiple muscle fibres controlling the eyeball to the nervous system function together to send and receive necessary electrical signals to and from the brain. It results in action potential to facilitate the reaction or some body movement. The form of summation depends on the frequency of the electrical signal, and hence the nerve cells distinguish between a temporal and spatial summation.
Difference
Temporal Summation
- Temporal summation is the type of summation in which a single stimulus is added in a short time.
- A single presynaptic neuron takes up the role of producing the action potential.
- Singular presynaptic neurons facilitate the generation of sub-thresholds over a period.
- It is a less efficient process as it requires some time to generate an action potential.
- The summation of stimulus increases depending on cell membrane time constant length.
- Such a form of summation occurs at a high frequency of electrical signals reaching the brain.
In skeletal muscle units, the force experienced by the muscles is controlled by changing the frequency of action potentials reaching the muscle fibres. The lower levels of action potential create a low concentration in the muscle, which prevents damage to the muscle tissues and surrounding skeletal structure.
Spatial Summation
- A spatial summation is a form of sensory summation in which several stimuli are added in a short time.
- Various stimuli from multiple cells combine at the presynaptic neurons to generate action potentials.
- Multiple presynaptic neurons are added to generate a sub-threshold.
- It is a more efficient process as it takes less time to generate action potentials.
- Reaching action potential depends on how close the input is to the axon hillock.
- The spatial summation can occur even at low frequencies as the number of electrical signals received per unit time is high.
Temporal and Spatial summation depends on the number of stimuli and the time to receive each successive signal. One presynaptic neuron is involved in temporal summation, and spatial summations are involved. Still, the final goal of both of these works is to generate enough action potentials to stimulate the motor nerves. Both summation forms minutely differ, so you must also pay attention to the similarities.
Learn how to acknowledge any source of information using the APA 7th style.
Download Now
Explain the Mechanism Of Postsynaptic Summation And Action Potentials?
The basic mechanism of the postsynaptic potential can be divided into three sub-portions depending on the input, integration and generation processes.
- The part of the motor neuron responsible for receiving or inputting the incoming electrical signals is called the input section. It contains the dendritic and somatic domains with an ion channel activated by neurotransmitters.
- When the input section is at work, a postsynaptic potential is generated. The generation of action potentials heavily depends on activating the ion channels in the input zone. The integrative section is composed of the axon hillock domain that adds the postsynaptic potential to generate an action potential.
- The generation unit consists of the axon domains responsible for action potential generation.
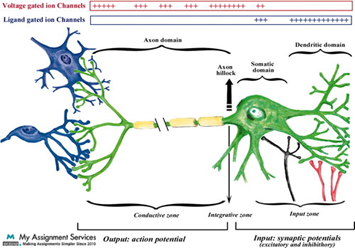
The summation of various postsynaptic potentials allows the neuron to generate an electrical signal, and the inhibitory and the excitatory synapses react. The final sum of synaptic inputs produces action potentials that further depend on the balance between inhibition and excitation. The results achieved by adding all excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials must be sufficient to achieve the threshold required for generating action potentials. Generally, the balance between the inhibitory and excitatory potentials continually changes depending on the number of synapses active at a certain time.
The summation is vital for body movements in humans and as the proper body movements depend on the correct timing and generation of action potential to regulate various movements. Athletes and professional sports players spend countless hours training their bodies to bear the stress of extreme and rapid movements and train their brains to stimulate the neurological system to generate desired force and body movement.
New innovative research has developed brain-computer inference technology, enabling patients to use their brain electrical signals to control a computer. Such groundbreaking innovations are a good example of signal summation, the next big step in medical science.
Simultaneous summation happens when an athlete moves multiple parts of the body together. Also known as spatial summation, it generates multiple stimuli simultaneously that produce action potential quickly to facilitate the athlete’s body movements. An example of temporal summation can be the activities that require less body movement, like reading. People usually sit in a quiet, deserted space for reading. Such spaces only activate the visual stimuli, and hence more time is taken to produce action potentials.
Read more of our live blogs and become a part of the trending discussion among students worldwide. Get expert insights on manifold courses and affordable academic writing assistance only at the My Assignment Services website. Enrol today to access our extensive library that holds free sample case studies, books, sample solutions, and more.
Related Study Materials
Our Experts can answer your Assignment questions instantly.
Ask Question0 Comment
Get It Done! Today
1,212,718Orders
4.9/5Rating
5,063Experts













Loved reading this Blog? Share your valuable thoughts in the comment section.
Add comment